Female Fertility
Disease Background

- Infertility is defined as the failure to achieve a pregnancy after ≥12 months of regular unprotected sexual intercourse (WHO).
- Women’s disorders caused ~40% of infertility cases. Some of the leading diseases include endometriosis (20-50%) [1], PCOS (30-60%) [2], fibroids (5-10%) [3], pelvic inflammatory disease, and others. BV is also prevalent among infertile women (10-20%) [4] and is a leading cause of adverse pregnancy outcomes.
- ART (Assisted Reproductive Technology) is a major type of treatment to help infertile patients get pregnant, others include drug treatment, surgery, and more.
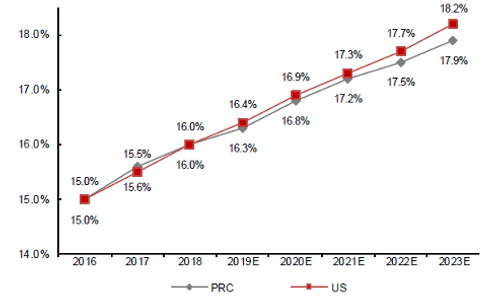
Infertility Rate in China and US [5]
- Infertility has been increasingly prevalent globally due to the increasing average age of first birth, unhealthy lifestyle, and environmental pollution.
- From ~11% in 1997, the infertility rate is expected to reach ~18% in 2023 in both China and US and may continue to grow.
Major Treatment: Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART)
In-vitro Fertilization (IVF)
- Eggs are retrieved and fertilized outside women’s body in a lab setting, and embryos are transferred back to women womb 3-5 days after fertilization to continue development.
- Traditional IVF-ET (Embryo Transfer) is mostly used, and Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI, when sperm quality is low) and Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT, check for chromosomal disorders or genetic diseases) can add to the IVF procedure to improve outcome in certain patients.

Artificial Insemination
- Deposit sperms from a woman’s mate (Artificial Insemination by Husband, AIH) or a donor (Artificial Insemination by Donor, AID) directly into the uterus to achieve natural fertilization and pregnancy.
- Suitable for infertility door to poor sperm quality.
Major Treatment: Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART)

In-vitro Fertilization (IVF)
- Eggs are retrieved and fertilized outside women’s body in a lab setting, and embryos are transferred back to women womb 3-5 days after fertilization to continue development.
- Traditional IVF-ET (Embryo Transfer) is mostly used, and Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI, when sperm quality is low) and Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT, check for chromosomal disorders or genetic diseases) can add to the IVF procedure to improve outcome in certain patients.
Artificial Insemination
- Deposit sperms from a woman’s mate (Artificial Insemination by Husband, AIH) or a donor (Artificial Insemination by Donor, AID) directly into the uterus to achieve natural fertilization and pregnancy.
- Suitable for infertility door to poor sperm quality.
Unmet Needs
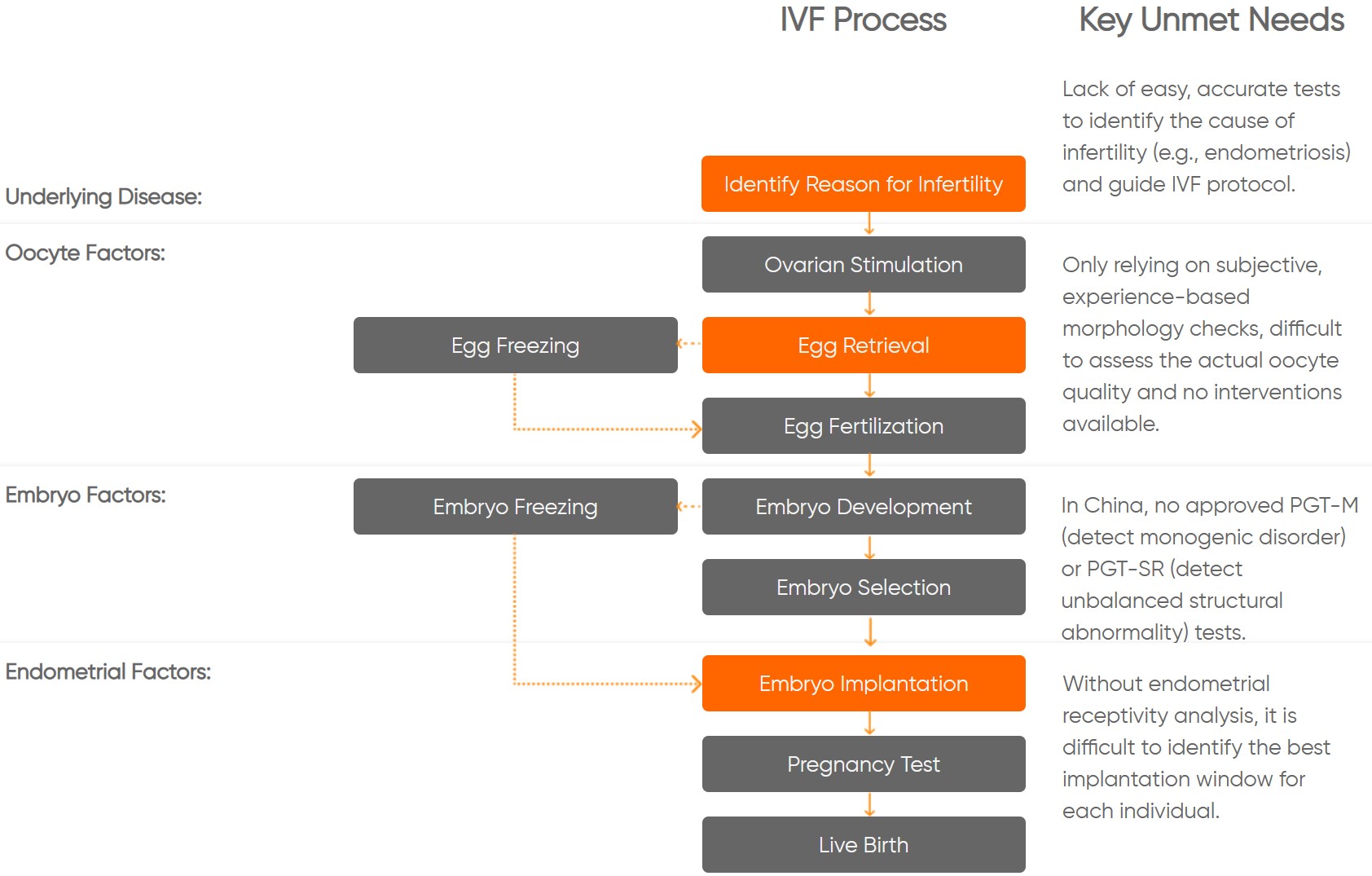
The IVF market is rapidly growing, but the success rate is still far from satisfactory. The process for IVF remains largely a “black-box” and lacks reliable check-points throughout the process.
Unsatisfied Success Rate
Unmet Needs In IVF Process
IVF Process
Key Unmet Needs
Sources
[1]. 子宫内膜异位症相关不孕诊治指南解读2018.
[2]. 多囊卵巢综合征的诊治进展2020.
[3]. Guo XC, Segars JH. The impact and management of fibroids for fertility: an evidence-based approach. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am. 2012 Dec;39(4):521-33.1
[4]. Van Oostrum N, et al, Risks associated with bacterial vaginosis in infertility patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Hum Reprod. 2013 Jul;28(7):1809-15.
[5]. Frost & Sullivan report. Picture is from aveya.in
[6]. 2021中国女性生理健康白皮书.
[7]. 2022中国育龄女性生殖健康研究报告.
[8]. 平安证券2021辅助生殖行业全景图.
[9]. US CDC ART Success Rates.
[10]. 中华医学会生殖医学分会:2019年辅助生殖技术 数据报告.
[11]. MMWR Surveill Summ. 2022 Feb 18;71(4):1-19.
[12]. 中国卫生事业管理, 2021, 38(6).
[13]. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2022 Feb;39(2):305-313.


